As artificial intelligence becomes a core part of modern business operations, its role in managing customer data is expanding rapidly.
From powering chatbots to delivering hyper-personalized user experiences, AI systems process vast amounts of personal information every second.
But with great capability comes great responsibility—especially when it comes to protecting customer privacy and ensuring data security.
This article breaks down how AI handles customer data behind the scenes, the safeguards in place to protect user information, and how businesses can use AI to personalize interactions without crossing ethical lines.
Whether you’re navigating data-driven strategies or simply want to understand how your information is used, this guide offers a clear, updated look into the intersection of AI, privacy, and trust.
What is customer data?
Customer data refers to the wide range of information that businesses collect from and about their customers through various interactions—both online and offline.
This data is a valuable asset, helping organizations understand their audience, tailor their services, and make smarter business decisions.
Whether someone browses a website, makes a purchase, or fills out a feedback form, they’re contributing to a growing digital profile. Businesses analyze this data to improve customer experiences, develop targeted marketing, and drive long-term loyalty.
Key Categories of Customer Data (with Examples)
1. Identity Data
This is the foundational data that identifies who a customer is.
Common examples:
- Name and surname
- Email address or phone number
- Date of birth
- Home or billing address
- Demographics such as gender, age, or nationality
Use case:
A subscription service uses this information to create user accounts and personalize content delivery.
2. Engagement Data
This type of data captures how a customer interacts with your brand across channels and touchpoints.
Examples:
- Pages visited on a website or app
- Click paths and navigation behavior
- Interaction with emails, ads, or push notifications
Use case:
An online retailer uses engagement data to optimize product page layouts and improve user experience.
3. Purchase Data
These are records of a customer’s financial activity with a brand.
Examples:
- Products bought or services subscribed to
- Purchase dates and amounts
- Payment preferences
- Refund or exchange history
Use case:
A loyalty program uses this data to reward repeat buyers with discounts or exclusive offers.
4. Sentiment and Feedback Data
This involves insights into what customers think or feel about your brand.
Examples:
- Product reviews and testimonials
- Responses to satisfaction surveys
- Ratings or comments on social media
- Support inquiries or complaints
Use case:
A SaaS company reviews sentiment data to refine its onboarding process and reduce churn.
Why Customer Data Matters
Customer data is more than just information—it’s the heartbeat of a customer-centric business.
In today’s competitive digital environment, collecting and using customer data effectively allows companies to create personalized experiences, make smarter decisions, and stay ahead of the curve. Here’s why it plays such a crucial role:
1. Enables Personalized Experiences
Customers no longer settle for one-size-fits-all experiences. They expect businesses to understand their needs and tailor interactions accordingly. Customer data makes this possible by revealing preferences, habits, and interests.
Example:
An online clothing store recommends styles based on browsing and purchase history, creating a curated shopping experience.
Impact:
More relevant content, increased engagement, and higher chances of repeat purchases.
2. Drives More Effective Marketing
Data-backed marketing is not only more accurate—it’s more cost-effective. When companies understand their audience, they can craft messages that resonate and reach the right people at the ideal time.
Example:
A travel company targets users who searched for beach destinations with a limited-time offer on tropical vacation packages.
Impact:
Improved targeting, stronger ROI, and better conversion rates.
3. Strengthens Customer Loyalty and Retention
Monitoring customer behavior helps identify trends that indicate satisfaction—or dissatisfaction. Businesses can then take action to improve the experience, fix problems, or reward loyalty before customers walk away.
Example:
A subscription service notices that users are canceling after three months and sends exclusive renewal perks before that point.
Impact:
Lower churn rates and longer-lasting customer relationships.
4. Guides Product Improvements and Innovation
Customer data is a direct line to what users want. By analyzing how people interact with products or services, companies can spot improvement areas and introduce features that truly add value.
Example:
A mobile app uses feedback and in-app activity to identify confusing features and release simplified updates.
Impact:
Higher product adoption, fewer support requests, and better user satisfaction.
5. Supports Fast, Informed Customer Service
With access to detailed customer profiles, support teams can deliver faster and more relevant assistance. AI tools powered by historical data can even anticipate questions and suggest solutions in real-time.
Example:
A helpdesk chatbot automatically pulls up a user’s last order when they ask about delivery status.
Impact:
Fewer delays, personalized service, and happier customers.
6. Creates a Competitive Edge
In industries where customer preferences shift quickly, having real-time data insights can be the difference between leading and lagging.
Companies that know how to turn data into action tend to innovate faster and respond better to market changes.
Example:
A grocery delivery service uses buying patterns to optimize local inventory, cutting delivery times and increasing customer satisfaction.
Impact:
More agile operations, better decision-making, and stronger market positioning.
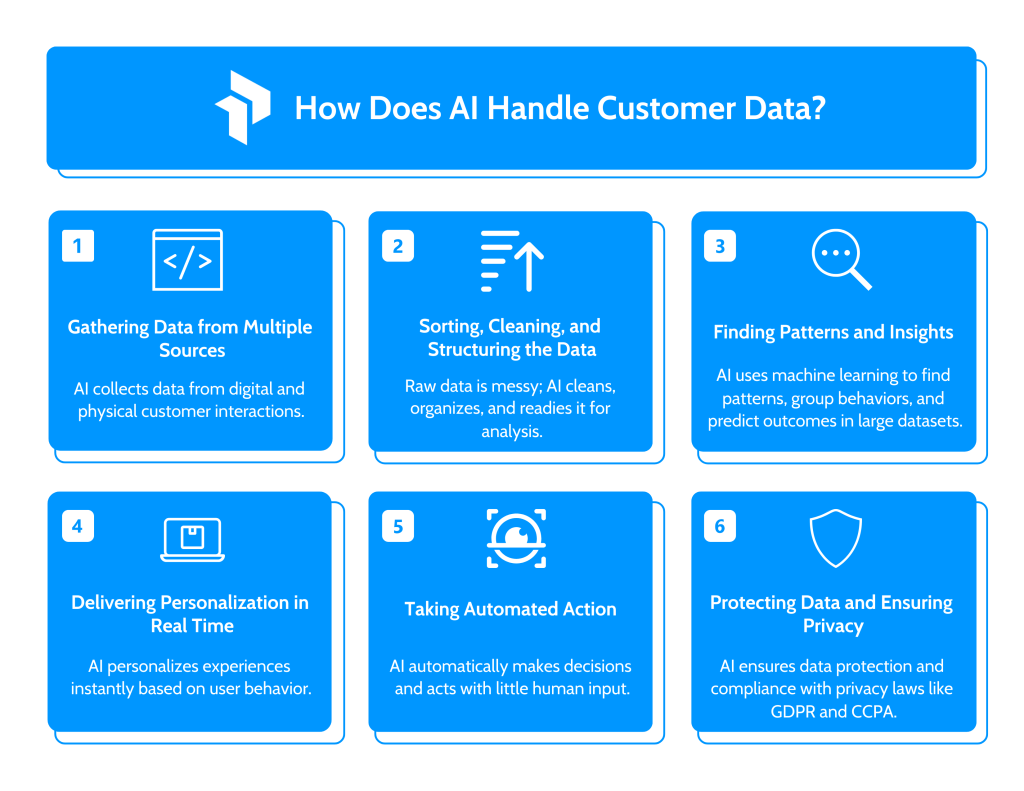
How Does AI Handle Customer Data?
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing how businesses understand and interact with their customers.
From collecting raw information to creating personalized experiences in real time, AI plays a central role in turning data into actionable insights. But how exactly does it work behind the scenes?
Let’s break down the process AI follows when handling customer data—along with the key considerations for privacy, accuracy, and responsible use.
1. Gathering Data from Multiple Sources
AI systems begin by pulling in data from a wide variety of touchpoints. This includes digital platforms like websites and apps, as well as physical interactions through in-store purchases or call center conversations.
Where AI collects data:
- Online orders and browsing history
- Customer emails and live chats
- Feedback forms and product reviews
- Mobile apps, smart devices, and CRM systems
AI’s Function:
Uses advanced algorithms to scan, capture, and organize both structured data (like purchase totals) and unstructured data (like open-ended feedback).
2. Sorting, Cleaning, and Structuring the Data
Raw data is often messy. AI uses intelligent systems to organize this information, correct inconsistencies, remove duplicates, and prepare it for deeper analysis.
AI’s Role:
- Identifies and corrects flawed or missing entries
- Standardizes data formats for consistency
- Transforms unstructured input (like voice or text) into machine-readable formats
Why it’s important:
Clean, reliable data forms the foundation of any successful AI-driven decision.
3. Finding Patterns and Insights
AI is particularly powerful at identifying hidden trends within massive datasets. Using machine learning, it can discover correlations, group similar behaviors, and predict outcomes based on historical data.
Common AI analyses:
- Clustering customers based on buying habits
- Forecasting product demand
- Detecting behavior changes that signal churn
Tools in use:
Neural networks, supervised learning, unsupervised clustering, and regression models.
4. Delivering Personalization in Real Time
AI goes beyond analysis—it actively shapes customer experiences. As a user interacts with a brand, AI adjusts content, offers, and recommendations on the fly based on that customer’s behavior and profile.
Examples of AI-driven personalization:
- Recommending similar products after a purchase
- Adjusting homepage content based on past visits
- Sending tailored promotions based on location and interest
Result:
A smoother, more relevant experience that keeps customers engaged and coming back.
5. Taking Automated Action
AI isn’t just observing—it’s making decisions and taking action automatically. Once trained on customer data, AI systems can execute workflows with minimal human involvement.
Examples:
- Triggering an email when a customer abandons a cart
- Flagging suspicious activity in a user’s account
- Routing support tickets to the appropriate department based on sentiment analysis
Benefit:
Quicker responses, better customer service, and more efficient operations.
6. Protecting Data and Ensuring Privacy
Handling customer data comes with great responsibility. AI helps enforce data protection policies and compliance with global privacy regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and others.
How AI supports security and compliance:
- Detects unauthorized access attempts
- Monitors systems for anomalies or data leaks
- Encrypts data and enforces access controls
Best Practices:
- Be transparent with customers about data use
- Only collect the information you need
- Give users control over how their data is handled
Q&As
1. What kinds of customer information does AI work with?
AI processes diverse data types such as personal details, purchase records, browsing activities, customer feedback, and interactions from support channels.
2. How does AI gather customer information?
AI collects data from digital platforms like websites and mobile apps, social media, customer databases, chatbots, and connected devices.
3. What happens to raw customer data once AI receives it?
AI organizes the data by cleaning errors, removing duplicates, filling in missing pieces, and converting messy inputs into structured formats ready for analysis.
4. Can AI interpret data that isn’t neatly organized?
Absolutely, AI uses technologies like natural language processing and image recognition to analyze text, audio, images, and other unstructured data.
5. How does AI customize the customer experience?
By studying patterns in data, AI tailors recommendations, content, and communications to match individual customer preferences in real time.
6. Is AI capable of making automatic decisions based on customer data?
Yes, AI can autonomously trigger actions such as sending personalized offers, detecting fraud, or directing customer inquiries without manual input.
7. What measures does AI use to protect customer privacy?
AI incorporates encryption, role-based access, and compliance mechanisms to safeguard data in line with privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA.
8. How is machine learning involved in handling customer data?
Machine learning trains AI to recognize patterns, categorize users, predict future actions, and continuously improve through new data inputs.
9. How fast can AI respond using the data it processes?
AI operates in real time, enabling instantaneous analysis and responses that adapt to customer actions as they happen.
10. Does AI adhere to data privacy regulations when handling customer information?
When properly configured, AI complies with data protection laws by limiting data collection, ensuring user consent, and enabling data control options.
11. What process does AI follow to clean customer data?
AI detects inconsistencies, removes repeated entries, corrects inaccuracies, and normalizes data formats for accurate downstream use.
12. Can AI forecast customer actions?
Yes, AI uses historical data trends to anticipate behaviors such as purchasing patterns, likelihood of churn, and interest areas.
13. How does AI manage data coming from various sources?
AI merges and aligns data from multiple origins—websites, social media, CRM tools—creating a comprehensive, unified view.
14. How secure is AI when managing sensitive customer data?
AI strengthens security by continuously monitoring for unusual activities, automating threat detection, and enforcing strict access controls.
15. Is AI effective at identifying fraudulent behaviors?
Yes, AI analyzes transaction patterns and anomalies to quickly detect and prevent potential fraud.
16. How does AI address bias in customer data?
Developers employ techniques like balanced training datasets and fairness algorithms to minimize bias and promote impartial outcomes.
17. Does AI require human supervision in managing customer data?
While AI automates many tasks, human oversight remains essential to ensure ethical standards, handle exceptions, and refine AI accuracy.
18. What advantages does AI bring to handling customer data?
AI provides quick insights, personalized interactions, operational efficiencies, fraud protection, and proactive engagement strategies.
Leave a Reply